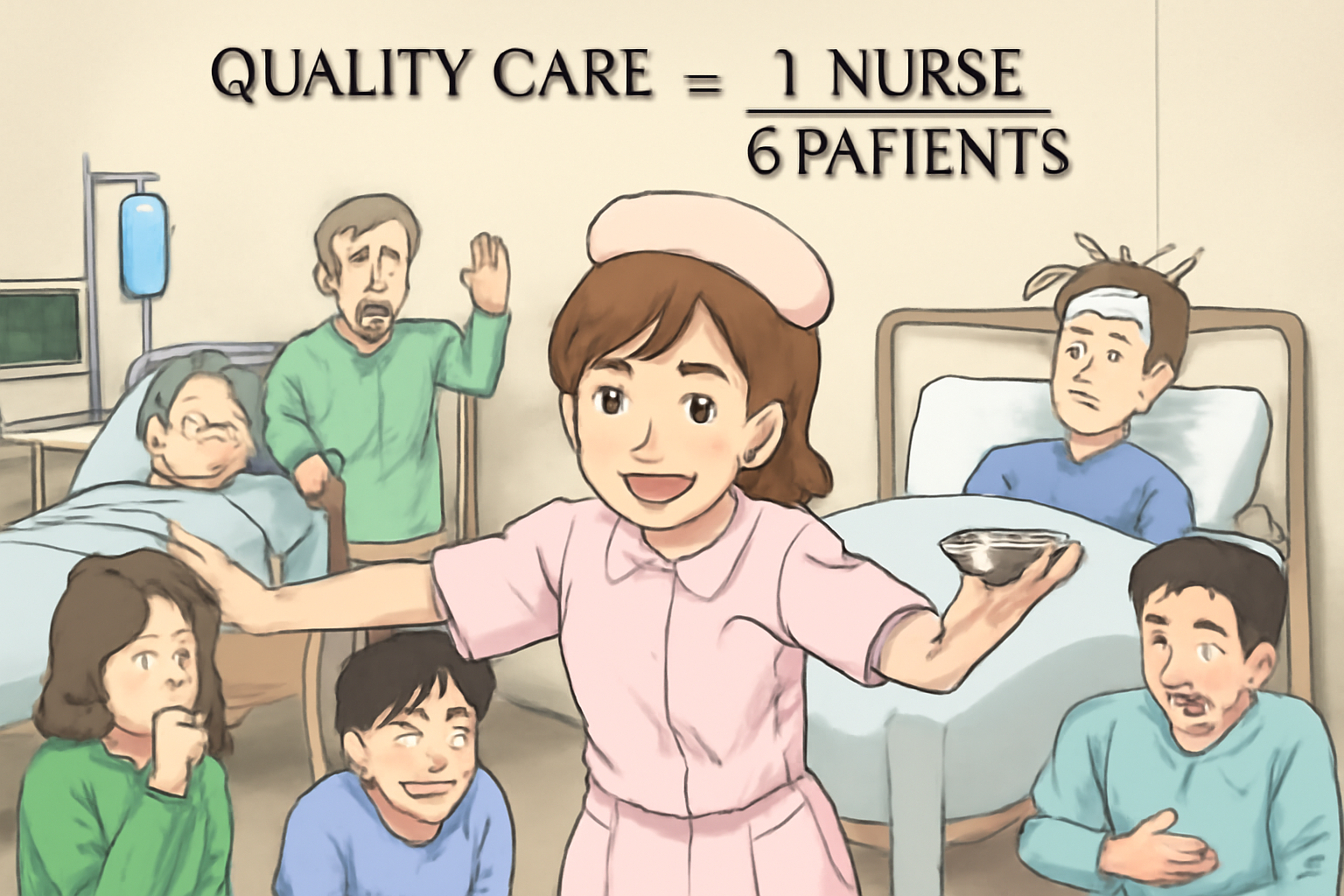
Care workers in various settings face numerous complex challenges that demand attention and strategic solutions. A prevalent issue is the high patient-to-caregiver ratio, which strains resources and limits the quality of attention each individual receives. The typical scenario involves a single care worker responsible for numerous residents, sometimes up to forty, which can significantly impact the level of personalized care each patient receives.
This imbalance often results from systemic issues, including underfunding and workforce shortages, which are persistent problems in the healthcare and care work industries. These factors contribute to high turnover rates among care workers, further exacerbating the issue as facilities struggle to maintain a workforce sufficient to meet resident needs.
The physical and emotional demands placed on care workers in such conditions are immense. They must frequently perform physically demanding tasks, often without adequate support or equipment, leading to increased risk of injury. Furthermore, the emotional toll of being unable to provide the level of care they aspire to deliver can contribute to work-related stress and burnout.
Training and professional development opportunities for care workers are frequently limited, hindering their ability to cope with the complexity of resident needs effectively. This deficiency can affect the quality of care and the satisfaction of both workers and residents.
Legislative and policy reforms are imperative to address these challenges. Improved funding and investment in the care workforce can help lower the patient-to-caregiver ratio, enhancing care quality and worker satisfaction. Additionally, increasing remuneration and providing career advancement opportunities may attract more individuals to the profession and encourage retention, fostering a more sustainable workforce.
Innovative solutions, such as technology integration in care environments, can also alleviate some pressures by improving efficiency and allowing workers to focus more on high-value tasks. However, these advancements must be implemented thoughtfully, with adequate training and support to ensure their effectiveness and sustainability.